This article is designed to help you uncover potential reasons why you might be having trouble with Google not indexing your site. Sometimes the issues can be a quick fix, however, there are times when you must dig deeper to uncover the true cause of Google not indexing all of your web pages.
What is Googlebot?
Googlebot refers to Google’s web crawling bot or “spider”, which is encumbered with the task of fetching billions of pages on the web. Every time it crawls a website, the Googlebot discovers new and updated content to add to the Google Index, which is then processed to become searchable by people.
An algorithmic process is used to determine the sites to be crawled, the crawl frequency, and the number of pages to be fetched from each site.
Identifying Crawling Problems
Start your investigation by simply typing site:yoursite.com into the Google search bar. Does the number of results returned correspond with the amount of pages your site has, give or take? If there’s a a large gap in the number of results versus the actual number of pages, there might be trouble in paradise. (Note: the number given by Google is a ballpark figure, not an exact amount). You can use the SEO Quake plugin to extract a list of URLs that Google has indexed. (Kieran Daly made a short how-to list in the Q&A section on this).
The very first thing you should have a look at is your Google Search Console dashboard. Forget about all the other tools available for a second. If Google sees issues with your site, then those are the ones you’ll want to address first. If there are issues, the dashboard will show you the error messages.

Here’s 10 errors that doesn’t make Google index your website
1. Blocked via Robots.txt
Your website’s /robots.txt file (located at http://www.domain.com/robots.txt, for example) gives Google its crawl commands. If a particular page on your site is missing from Google’s index, this is one of the first places to check. Google may show a message reading “A description for this result is not available because of this site’s robots.txt” under a URL if it previously indexed a page on your site that is now blocked via robots.txt.
2. Noindex” X-Robots Tag
Similar to a meta robots tag, an X-robots tag offers the ability to control indexation with Google via a page-level tag. However, this tag is used in the header response of a particular page or document. It is commonly used on non-HTML pages where there is no <head>, such as PDF files, DOC files, and other files that webmasters wish to keep out of Google’s index. It’s unlikely that a “noindex” X-robots tag has been accidentally applied, however you can check using the SEO Site Tools extension for Chrome
3. “Noindex” Meta Robots Tag
Another common reason why a page on your site may not be indexed in Google is that it may have a “noindex” meta robots tag of sorts in the <head> of the page. When Google sees this meta robots tag, it’s a clear directive that it should not index the page. Google will always respect this command, and it can come in a number of forms depending on how its coded:
- noindex,follow
- noindex,nofollow
- noindex,follow,noodp
- noinde,nofollow,noodp
- noindex
4. Response Codes Other than 200 (OK)
Perhaps it goes without saying, but if your pages don’t produce a 200 (OK) server response code, then don’t expect search engines to index them (or keep them indexed if they once were). Sometimes URLs accidentally get redirected, produce 404 0r 500 errors depending on CMS issues, server issues, or user error. Do a quick check to ensure that the URL for your page is loading properly. If it loads, and you see it, you’re probably fine. But, you can always run URLs through HTTPStatus.io to verify.
5. You’re being blocked by htaccess or privacy settings.
If you run a WordPress site, it’s possible you accidentally have privacy settings on—you can toggle this off by checking out “Privacy” under the Settings tab. It’s also possible that you’re using a .htaccess file for your website on the server. While .htaccess files are useful in most cases, they can sometimes interfere with site indexing.
6. External Duplicates
External duplicate content is what you might expect…content duplicated with other websites. Large ratios of duplicate content are a sure sign of low quality to Google, and should be avoided at all costs. No matter whether your website is a lead generation marketing site, E-Commerce store, online publishing platform, or hobbyist blog…the same rules apply.
One way to tell if your content is duplicated with other sites is to put a snippet of content in quotes and search Google, such as this example, which shows that Home Depot’s product description is duplicated with a number of other websites. Note: Due to Home Depot’s brand authority, review content and other factors, they are likely to still rank well in Google’s search results with duplicate content. However, less authoritative sites may not be indexed fully nor rank well with duplicate content such as manufacturer-supplied product descriptions.
7. Internal Duplicates
Internal content duplication is a risk to any SEO efforts. Internal duplicate content may or may not keep your pages out of Google’s index, but large ratios of internal duplicate content on your pages will likely keep them from ranking well. If you have a particular page that has a large amount of similar content with another page on your website, it’s possible that this could be the reason that your page is either not indexed in Google or simply not ranking well.
To check for internal duplicate content, I recommend using the Siteliner tool to crawl your website. It will report all pages with internal duplicated content, highlighting content that is duplicated for easy reference, and also offer you a simple graphical view of how much content is duplicated on your website.
8. Duplicate content is interfering with crawlers.
If you’re following best practices for content marketing, this shouldn’t be an issue, but there are circumstances where duplicate content can exist on your site—such as variations of a “master page” designed for slightly different audiences. If Google detects multiple instances of duplicate content, search engine crawlers can become confused and abandon indexing your site altogether. The easiest way to correct this is to get rid of the duplicate content. If deleting the duplicate content altogether isn’t an option, you can use 301 redirects or selective robots.txt files to ensure that Google only crawls one instance of each page.
9. You’ve been hit with a massive penalty.
When Google penalizes sites, it usually does so by dropping ranks and thus, visibility and traffic. However, there are rare and extreme cases when Google penalizes a site by completely removing it from indexes entirely. This is a type of manual penalty reserved for major infractions, so you don’t have to worry about this unless you’ve done something very wrong in the eyes of Google. If you’ve gotten deindexed this way, you’ve probably already been notified by Google, so unless that’s the case, you don’t have to worry that you’re not being indexed as a punishment.
10. Technical reasons for slow crawling
The technical reasons for Google to crawl your site slowly can be divided into three groups: your site is too slow, you have too many errors, or you have too many URLs.
Your server is slow
The main reason why we see Google crawling sites slowly, is when the site itself is actually slow. Google actually indicates this to you when this is the case, on the “crawl rate” page of Google Search Console. If this is the case, Google might show you a “faster” option:
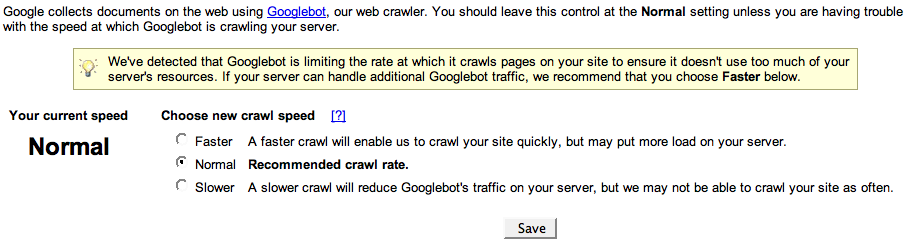
Our advice: set it to “Faster”, but don’t stop with that: make your server respond faster, either by upgrading your hosting, or improving your site’s caching. Chances are that when Google is suffering long load times, your users are as well.
Too many errors on your site
If you have a lot of errors on your site for Google, Google will start crawling slowly too. To speed up the crawl process, fix those errors. Simply 301 redirect those erroring pages to proper URLs on your site.
If you don’t know where to find those errors: use the Google Search Console integration in Yoast SEO. Or log into Google Search Console. If you have access to your site’s access logs, you can also look at those, preferably with a tool like Screaming Frog’s Log file analyzer.
To prevent your site from being crawled slowly, it’s important that you regularly look at your site’s errors and fix them. We have a more extensive article on fixing 404 errors.
When your site is down too much, Google will slow down incredibly hard. If this happens because of your hosting, switch hosting. Make sure to check on your site’s uptime with a tool like Pingdom.
Too many URLs
If you simply have too many URLs on your site, Google might crawl a lot but it will never be enough. This can happen because of faceted search navigation for instance, or another system on your site that simply generates too many URLs. To figure out whether this is the case for you, it’s always wise to regularly crawl your own site. You can either do that manually with Screaming Frog’s SEO spider, or with a tool like Ryte.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We provide the best quality backlinks as ever, pls contact us qualitybacklink.net@gmail.com ; Skype: qualitybacklink






